Squeezed Very Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification
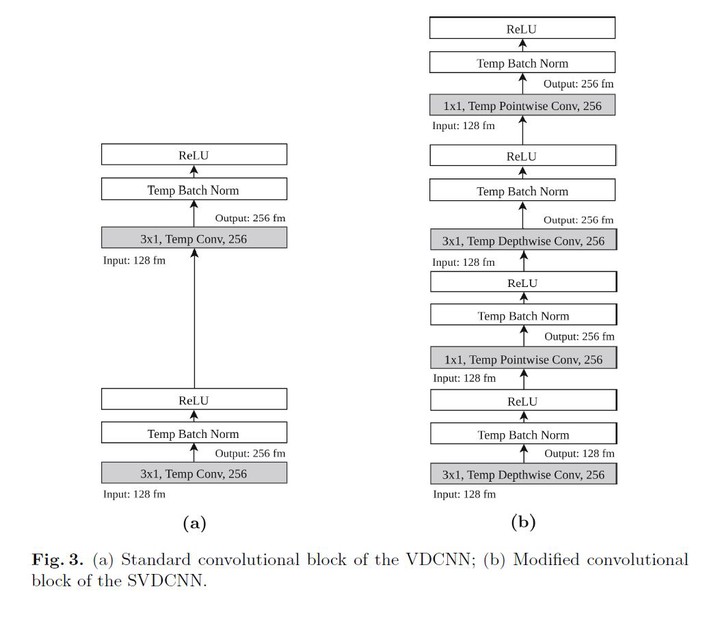 Photo by Authors
Photo by AuthorsEmbedding artificial intelligence on constrained platforms has become a trend since the growth of embedded systems and mobile devices, experimented in recent years. Although constrained platforms do not have enough processing capabilities to train a sophisticated deep learning model, like convolutional neural networks (CNN), they are already capable of performing inference locally by using a previously trained embedded model. This approach enables numerous advantages such as privacy, response latency, and no real time network dependence. Still, the use of a local CNN model on constrained platforms is restricted by its storage size. Most of the research in CNNs has focused on increasing network depth to improve accuracy. In the text classification area, deep models were proposed with excellent performance but relying on large architectures with thousands of parameters, and consequently, high storage size. We propose to modify the structure of the Very Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (VDCNN) model to reduce its storage size while keeping the model performance. In this paper, we evaluate the impact of Temporal Depthwise Separable Convolutions and Global Average Pooling in the network parameters, storage size, dedicated hardware dependence, and accuracy. The proposed squeezed model (SVDCNN) is between 10x and 20x smaller than the original version, depending on the network depth, maintaining a maximum disk size of 6MB. Regarding accuracy, the network experiences a loss between 0.4% and 1.3% in the accuracy performance while obtains lower latency over non-dedicated hardware and higher inference time ratio compared to the baseline model.